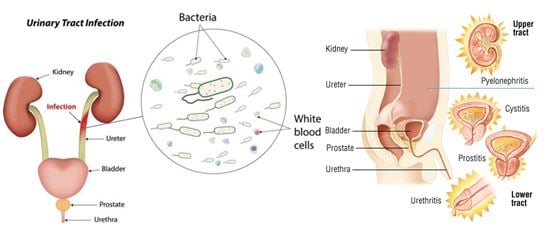
Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection from microbes. These are organisms that are too small to be seen without a microscope. Most UTIs are caused by bacteria, but some are caused by fungi and in rare cases by viruses. UTIs are among the most common infections in humans.
A UTI can happen anywhere in your urinary tract. Most UTIs only involve the urethra and bladder, in the lower tract. However, UTIs can involve the ureters and kidneys, in the upper tract. Although upper tract UTIs are more rare than lower tract UTIs, they’re also usually more severe.
What are the symptoms?
Symptoms of a UTI depend on what part of the urinary tract is infected.
Lower tract UTIs affect the urethra and bladder.
Symptoms of a lower tract UTI include
- Burning with urination
- Increased frequency of urination without passing much urine
- Increased urgency of urination
- Bloody urine
- Cloudy urine
- Urine that looks like cola or tea
- Urine that has a strong odor
- Pelvic pain in women
- Rectal pain in men
Upper tract UTIs
They affect the kidneys. These can be potentially life threatening if bacteria move from the infected kidney into the blood. This condition, called urosepsis, can cause dangerously low blood pressure, shock, and death.
Symptoms of an upper tract UTI include
- Pain and tenderness in the upper back and sides
- Chills
- Fever
- Nausea
- Vomiting
What are the Causes and risk factors of an UTI
- Age — older adults are more likely to get UTIs
- Reduced mobility after surgery or prolonged bed rest
- Kidney stones
- A previous UTI
- Urinary tract obstructions or blockages, such as an enlarged prostate, kidney stones, and certain forms of cancer
- Prolonged use of urinary catheters, which may make it easier for bacteria to get into your bladder
- diabetes, especially if poorly controlled, which may make it more likely for you to get a UTI
- Pregnancy
- Abnormally developed urinary structures from birth
- A weakened immune system
- Additional risk factors in women include naturally shorter urethra and decrease in estrogen levels. However, UTIs happen much more frequently in women than in men. The ratio is 8:1. This means that for every eight women who have UTIs, only one man does