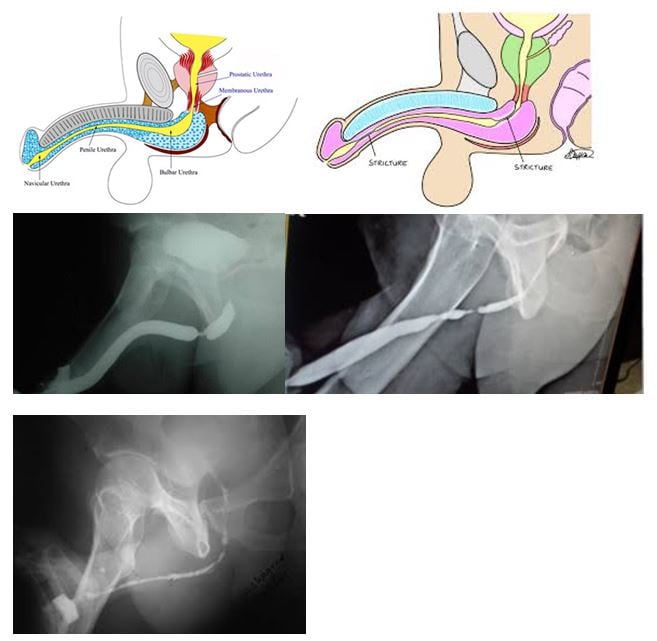
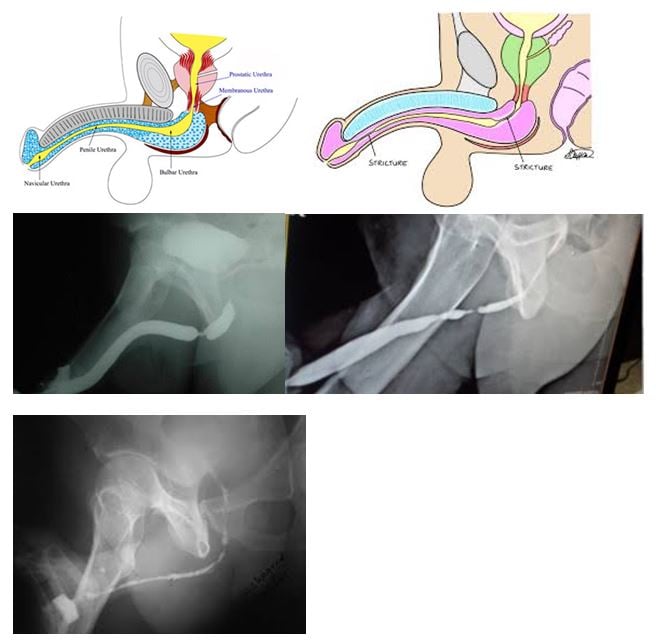
Urethral Stricture
A urethral stricture is scarring in or around the urethra (urine pipe draining urine out from the bladder) that narrows or blocks the passageway through which urine flows from the bladder. The length of strictures varies from less than 1 cm to the full length of the urethra and is much more common in men than in women and can occur anywhere between the bladder and the tip of the penis. In addition to uncomfortable urinary symptoms such as reduced urine flow rate and more frequent urination, a urethral stricture can lead to complications that include urinary tract infections, prostate infections, complete blockage of urine and kidney damage.
Causes
The stricture results from
- Inflammation for e.g. radiotherapy
- Infection – sexually transmitted diseases such as gonorrhoea or chlamydia
- Injury – road traffic accidents, placement of a catheter, endoscope, or other foreign body, after prostate surgery or removal of kidney stones, or following reconstructive surgery for congenital abnormalities in children
In many cases, though, the cause is not apparent.
Symptoms
Symptoms of urethral strictures are mostly urinary – painful urination, reduced urine output, slow urine stream, spraying of the stream, incomplete emptying of the bladder, and inability topass urine, dribbling of urine, Frequency sometimes occurs (needing to pass urine more often than normal), urine infections, reduced force of ejaculation etc.Urinary tract infections are also common, and blood will occasionally appear in the urine.
Tests
Diagnostic tests include urinalysis, urine cultures, uroflowmetry studies (measuring the flow from the bladder), and post-void residual studies, in which an ultrasound measures the amount that is left after a normal voiding.A look into the urethra by a special thin telescope called a cystoscope will be needed to assess the stricture.
The ascending urethrogram or AUG and antegrade urethrogram are imaging techniques that can help to pinpoint the length, position, and severity of the stricture. This involves injecting contrast in to the urine pipe and taking x-rays.
Treatment Options
Treatment is usually advised to improve the flow rate of urine, to ease symptoms and to prevent possible complications. The choice of treatment depends largely on the length and severity of the stricture. In minor cases in which the complication risk is low, doing nothing may be the best option; more moderate or severe cases are best addressed using either a minimally invasive or open surgical approach.
Urethral dilatation
It involves gradually stretching the stricture using instruments inserted in to the urine pipe. It can be done under local or general anaesthetic. It can recur after dilatation and therefore, a repeat dilation is commonly needed every so often when symptoms recur. (Some people are given a self-lubricating tube (catheter) which they insert themselves regularly to keep a stricture dilated.)
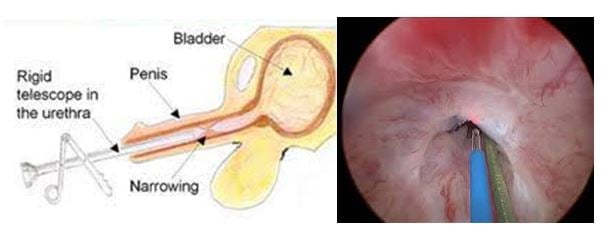
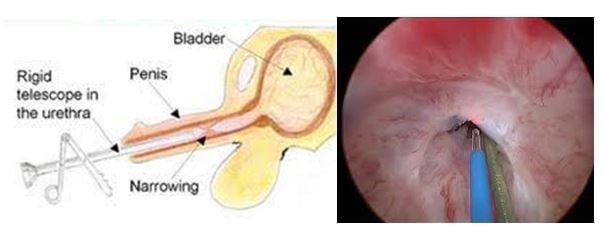
Internal Urethrotomy
In this procedure, a thin telescope is passed into the urethra to see exactly where the stricture is. This is done during a general anaesthetic. A tiny knife is then passed down the telescope to cut along the stricture. This widens the narrowed stricture. You will get relief of symptoms from this procedure. About half of people are cured for good by this procedure. However, like dilation, the stricture may re-form and the procedure may have to be repeated from time to time in some cases.
Cutting the stricture with a laser can also be done
Anastomotic urethroplasty
Surgically removing the stricture and then re-joining the ends are done for shorter strictures
Augmentation urethroplasty
The structured area is opened and the urethra widened by skin taken from inner lining of urethra(buccal mucosal urethroplasty), scrotum (dartos flap) or penile skin (for penile strictures). As a rule, there is a high success rate in curing symptoms with these operations.