Erectile Dysfunction
Difficulties in getting an erection
Inability to get or sustain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse is called erectile dysfunction. One in ten men will suffer from this and 1 in 3 diabetic men suffer from it.
How do erections happen?
A man needs hormones, blood supply, nerves and a desire if he is to achieve an erection. If one or more of these mechanisms fail then the erection will also fail.
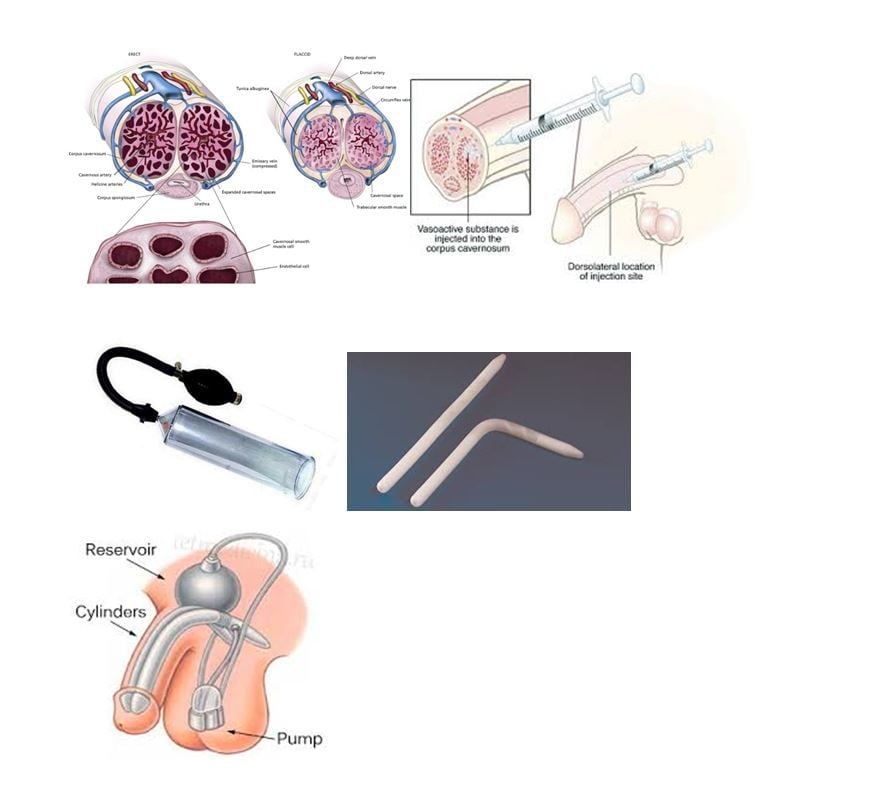
When aroused nerve impulses travel from the brain to the penis. This triggers the relaxation of the muscles in the penis which then allows increased blood flow into the tissues. As the penis fills with blood it will enlarge and become erect. As the penis enlarges it compresses the veins inhibiting blood flow out of the penis, thus sustaining the erection. The penis will stay erect until ejaculation or when arousal stops.
Causes
- Hormone imbalance – A deficiency of male hormones can reduce desire or interest in sexual function
- Nerve damage – damage to the nerves which cause the erection and reduced sensitivity thus making it increasingly difficult to achieve an erection
- Disease of the blood vessels – The blood vessels become narrowed and hardened. This reduces the blood supply to the penis. If the penis does not fill adequately then the veins will not be closed off and blood will leak out of the penis and the erection will not be maintained.
- Trauma– such as injury to the spinal cord
- Pelvic surgery Some operations on the prostate (radical prostatectomy, TURP), bladder or bowel may result in some nerve damage leading to impotence
- Drugs like for blood pressure, depression and sedatives have the side effect of causing impotence
- Smoking and alcohol
- Stress, depression, anxiety, relationship problems, embarrassment, guilt and other psychological issues
In men with diabetes the most common cause of erectile dysfunction is disease of the blood vessels and/or nerve damage.
Investigations
Clinical examination
Blood tests- measurement your lipids (cholesterol), blood sugar (diabetes check) and testosterone levels (hormone check), and measuring your blood pressure.
Penile doppler ultrasound before and after injection of a medicine in to penis to assess blood flow
Treatments
- General – Treatment of high cholesterol,diabetic control, blood pressure control and achieving adequate weight
- Counselling – especially if stress, anxiety and marital conflict are contributing to the problem
Medications
First-line treatment for most patients is now tablets. Three different medications are available at two different doses each. Urologist will advise to try at-least 4 doses of each medication before increasing the dose or trying different medications.
Hormone treatment This is offered to those patients who are deficient in male hormones i.e. testosterone. This treatment will not have any effect on those who do not have a hormone imbalance.
Self-injection therapy This treatment involves self injecting a drug into the side of the penis each time you want to have an erection. The injection causes the muscle in the penis to relax allowing increased blood flow into the penis.
Injection therapy is very affective for many men but some do find the very thought of self injection unacceptable. If you decide to choose this option then you will be trained in the clinic how to inject yourself.
Injection therapy can be used a maximum of twice a week and never more than once in 24hours. As with all drugs there are side effects. Occasionally the erection does not go down and you may need to come to hospital to have the erection reduced. This is not common.
Vacuum erection assistance devices These are a non-invasive method of getting and sustaining an erection. To use this device the penis is inserted into a cylinder, using plenty of lubrication to ensure a good seal at the base of the penis. A small vacuum pump is attached to the other end of the cylinder. The pump creates a vacuum and this causes blood to be drawn into the penis thus causing an erection. A constriction ring is then placed onto the base of the penis to trap the blood in the penis and maintain an erectile state. The cylinder is then removed. The ring can be left in place for up to 30 minutes.
Penile implants This involves surgical implantation of 2 rods into each side of the penis. They can be semi-rigid or inflatable and are permanent.
Penile implants are reserved for patients who have tried and failed other medical treatments such as tablets, injections, vacuum devices