Renal medicine is an intriguing and necessary discipline in the present day, given the rising frequency of metabolic syndrome and diabetes. It is critical to recognise renal illness early to treat or postpone the course of the disease.
Read More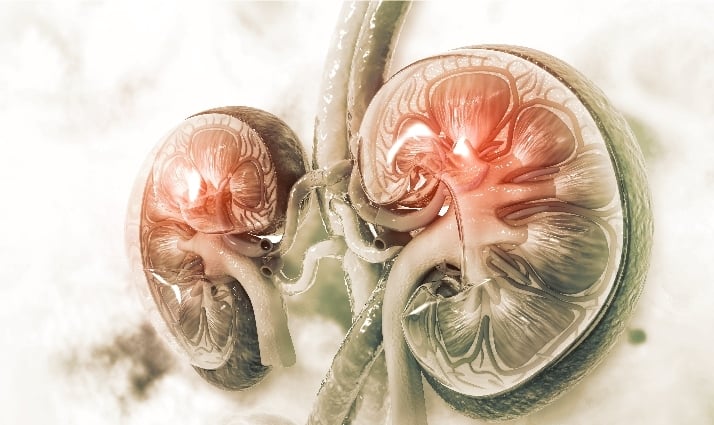
Renal medicine is an intriguing and necessary discipline in the present day, given the rising frequency of metabolic syndrome and diabetes. It is critical to recognise renal illness early to treat or postpone the course of the disease. Acute kidney damage may be recovered if detected early and the underlying causes are treated. In addition, we sometimes need to assist failing kidneys with renal replacement medicines.
Renal replacement treatment is required for people with chronic renal failure. Hemodialysis (blood purification using an extracorporeal machine), peritoneal dialysis (dialysis utilising the patient’s abdominal cavity), and renal transplant (implanting a new kidney into the patient’s body from a living or deceased donor) are all options. However, renal transplant is the most effective kind of renal replacement treatment.
Ultrasound abdomen, CT KUB with and without contrast, MRI abdomen, conventional renal angiograms, micturating cystourethrogram, intravenous urogram, and renal biopsy are all diagnostic options. In addition, renal biopsies are performed under ultrasound guidance, and angioembolisation of renal arteries is required in the event of excessive bleeding.
The kidneys are essential for life because of their sophisticated system of tubes and tubules that filter the blood of waste materials and excess water. In addition, the kidneys regulate fluid, electrolyte, and acid-base balance, which are affected by various medical states, medications, and poisons.
A renal transplant is a surgical procedure that involves implanting a healthy kidney from a living or deceased donor into a person whose kidneys are no longer functioning properly.
Bedwetting, also called nighttime incontinence or nocturnal enuresis – is passing urine in the night time in the bed while sleeping without realizing it.
The prostate gland is found only in men. It lies below the bladder. The tube which passes urine from the bladder (the urethra) runs through the middle of the prostate.
Difficulties in passing urine in males can be due to Urinary tract infections, prostate problems in older people and urethral stricture in younger people and ureteric stones. In some people, more than one condition is present.
Inability to get or sustain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse is called erectile dysfunction. One in ten men will suffer from this and 1 in 3 diabetic men suffer from it.
A circumcision is an operation to cut away the foreskin of the penis. The foreskin is the sleeve of loose skin that covers the end (head) of the penis.
The prostate gland is only found in men and lies at the base of your bladder and surrounds your urethra (tube that carries urine and semen out of your body).
TURP involves removal of the obstructing, central part of the prostate with telescope(cystoscope) and heat created by electric current(diathermy), creating a wide channel to allow urine to flow more easily.
This involves using a telescope (semi-rigid or flexible) passed into yourbladder through your urethra (waterpipe) to fragment and/or removestones from your ureter or kidney.
Patients can present to an urologist because they have noticed blood in the urine(visible haematuria), or after being referred by another doctor because urine routine tests have shown blood under the microscope (microscopic haematuria).
HolEP/ThulEP is a modern alternative to the standard Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP) procedure for bladder outflow obstruction due to prostate enlargement (BPH). It is a minimally invasive treatment for BPH done using laser.
Frequent urination also called frequency means having an urge to pass urine more often than usual. It can disrupt one’s normal routine, interrupt the sleep cycle, and it can be a sign of an underlying medical condition.It is normally only a problem if it affects a person’s quality of life or interferes with your routine work.
The pelvic floor is a complex layer of muscles and ligaments which stretches like a hammock from the pubic bone at the front of your pelvis to the coccyx at the bottom of your spine
Kidney stones in the urinary tract are common, between 8-15% of people will get a kidney stone in their lifetime.
The function of the kidney is to excrete waste products in the urine from your body. These waste products are in the form of salts like creatinine, sodium, uric acid, oxalate and others.
It is the complaint of involuntary leakage of urine during coughing or sneezing or any other strain like lifting weight. Stress incontinence is usually the result of the weakening of or damage to the muscles used to prevent urination, such as the pelvic floor muscles and the urethral sphincter.
Swelling or pain in the scrotum is one of the common reasons why patients see an urologist. Many times, it may coexist
Ureteric stones are very common especially in a hot country like India. Stones form in kidney and may remain there without giving trouble for many years. They can grow and when it becomes sufficient size can drop down into the tube draining urine from kidney (called ureter).
A urethral stricture is scarring in or around the urethra (urine pipe draining urine out from the bladder) that narrows or blocks the passageway through which urine flows from the bladder.
It is the complaint of involuntary leakage of urine accompanied by or immediately preceded by urgency.Urge incontinence is usually the result of overactivity of the muscles of the bladder (detrusor muscles), which control the bladder.
Urinary incontinence is the unintentional passing of urine.
There are several types of urinary incontinence
Urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection from microbes. These are organisms that are too small to be seen without a microscope. Most UTIs are caused by bacteria, but some are caused by fungi and in rare cases by viruses. UTIs are among the most common infections in humans.
PSA(Prostate Specific Antigen) is a small protein molecule which is released from the prostate gland into the bloodstream. As you get older, your prostate slowly enlarges and your PSA gradually increases. The larger your prostate, the higher the PSA.
You have been advised to have a nephrectomy by your urologist. This leaflet explains about the procedure and what to expect from the operation. This information in this leaflet is meant to be a guide only. Your urologist’s advise will be more accurate if there are discrepancies.
Nephrology is the study of the normal functioning of the kidneys as well as their disorders. The following illnesses are under the purview of nephrology:
Renal medicine is an intriguing and necessary discipline in the present day, given the rising frequency of metabolic syndrome and diabetes. It is critical to recognise renal illness early to treat or postpone the course of the disease. Acute kidney damage may be recovered if detected early and the underlying causes are treated. In addition, we sometimes need to assist failing kidneys with renal replacement medicines
Nephrology is an internal medicine speciality that focuses on the treatment of kidney problems. You have got two kidneys that are placed on either side of your spine, underneath your ribs.
Kidney stones occur when your urine contains more crystal-forming chemicals than the fluid in your urine can dilute, such as calcium, oxalate, and uric acid. Simultaneously, your urine may be lacking in chemicals that keep crystals from staying together, producing an ideal environment for kidney stones to grow.
You might be able to get around a little stone by drinking water. Drinking 2 to 3 quarts (1.8 to 3.6 litres) of water per day will dilute your pee and may prevent stones from developing. Unless otherwise directed by your doctor, drink enough liquids — preferably primarily water — to create clear or almost clear urine.

