What is Oral Thrush?
October 2, 2023
What is Oral Thrush
What is Thrush?
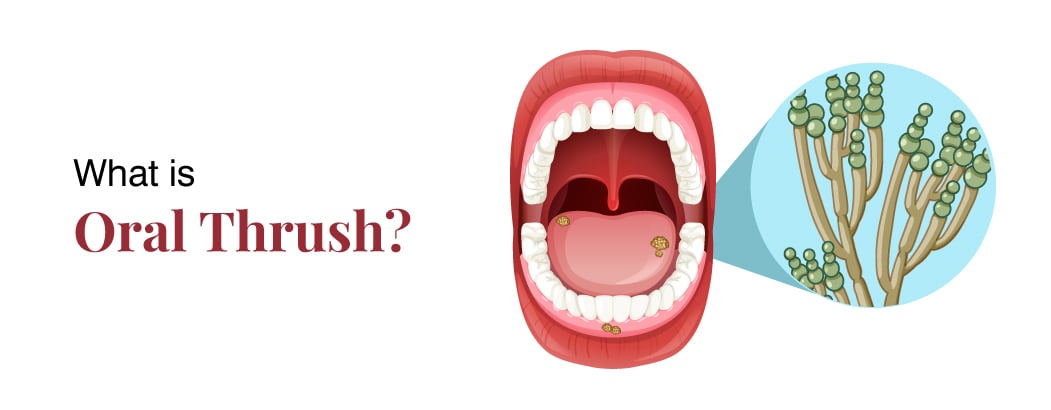
Thrush or oral thrush is an infection by fungus found inside the oral cavity including throat. It is mainly caused by the overgrowth of Candida yeast. Thrush is a condition that shows up as white patches, cream colonies or slightly raised lesions in the tongue, inner cheeks plus other internal parts of the mouth. However, these patches are not easy and usually cause pain and discomfort, for instance, while eating or swallowing. Thrush is usually linked to conditions such as lowered immunity, some drugs, and different diseases like diabetes and cancer. As a result, it requires anti-fungal medicines for treatment.
Table of Contents
- What is Thrush?
- Symptoms and Causes of Oral Thrush
- Diagnosis of Oral Thrush
- Treatment
- Risk factors
- Prevention Of Oral Thrush
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Oral Thrush: Symptoms and Causes
Symptoms:
- White Lesions: The primary symptom involves white, cottage cheese-like spots mainly on the tongue, inside the cheek and the roof of the mouth. Such lesions may look like raised cottages with a cream.
- Discomfort: Thrush (oral), though, is usually uncomfortable and may cause pain and a burning sensation inside the mouth (Corns et al). It may as well lead to difficulty in eating and swallowing.
- Altered Taste: At times, people who are affected by thrush lose the sense of taste or notice strange, metal-like taste in the mouth.
- Redness and Bleeding: The affected areas may develop into reddened lesions that ooze blood on contact.
Causes:
- Candida Overgrowth: Oral thrush has the underlying cause of candidiasis which is a yeast that is naturally found at the mouth. Thrush may result where Candida overgrows due to imbalance in the microorganisms’ numbers.
- Weakened Immune System: Some conditions cause the immune systems to become deficient thereby making one vulnerable to oral thrush (cancer, HIV/Aids as well as autoimmune disorders).
- Medications: Some drugs such as corticosteroid drugs, antibiotics and immunosuppressants interfere with the balance of microbes in the mouth and make it prone to candida overgrowth.
- Medical Conditions: The conditions that can lead to fungal overgrowth include diabetics, xerostomia, and hormonal changes.
- Tobacco Use: Oral thrush is more prone in smokers and users of tobacco products.
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Lack of adequate oral hygiene may provide suitable conditions for the development of Candida mostly with people wearing dentures.
- Inhaler Use: Moreover, some inhaler uses for asthma management might lead to oropharyngeal candidosis because of the effect of specific drugs on the oral microflora.
It’s essential to know these signs and causes as it requires immediate medical assistance when one has a weak immunity system and serious pain. Managing oral candidiasis requires appropriate treatment for the infection and dealing with any other issues in the mouth.
Diagnosis of Oral Thrush
There exists several ways of diagnosing oral thrush and they include both medical based and clinical tests done by trained health workers like Doctors and Dentists. The diagnostic process includes:
- Clinical Examination: A physical exam of the mouth will be done by the healthcare provider who also will look out for the common white lesions or other symptoms of oral thrush. A visual examination that forms part of the initial diagnostic process.
- Swab Tests: A confirmation of the presence of Candida can be made by taking a swab or a scraping from the white lesion. Following this, a sample is taken up to a lab for testing purposes. Specific type of Candida causing infection can be identified with microscopy and culture tests.
- Underlying Condition Evaluation: A healthcare provider can ask you about your previous ailments and your present health situation to check whether there is some other condition causing this infection.
Diagnosis of candidiasis is simple and the outcome of performed tests helps to identify a disease, determine its character and provide adequate therapy. Therefore, if you think that you have oral thrush or its signs, it will be important to consult with a doctor so as to make an exact diagnosis of the pathology and identify the causes.
Treatment
Fortunately, oral thrush is generally treatable and self-resolving. The main objective for treatment is to eradicate the Candida over-colonization and get rid of pain symptoms. Treatment options include:
- Antifungal Medications: Oral thrush is normally treated with antifungal drugs by physicians. They can come in different forms like oral suspensions, lozenges, and tablets. Nystatin, fluconazole and clotrimazole are common antifungal agents that are used in the treatment of yeast infection of the mouth. Take as directed, over the recommended period for better outcome.
- Proper Oral Hygiene: Oral thrush management and prevention require good oral hygiene habits. Brush your teeth daily using a soft bristle and non-abrasive paste. Ensure that you clean your dentures well, and also remove them every night so that your mouth can be given a chance of breathing.
- Rinse with Saltwater: A hot salted water gargle is an excellent way of easing mouth pain while accelerating healing. That is a simple but efficient home remedy.
- Managing Underlying Conditions: However, if the cause or the drug responsible for causing the Candida to invade is known, it might be addressed or changed by your care provider.
- Topical Antifungals: In certain instances, localized oral thrush may also be treated through the use of topical antifungal creams for infants. Such creams can be rubbed directly into the affected part of one’s mouth.
- Dietary Changes: Consuming low sugar products may be a way towards such an environment. Go with a healthy and balanced diet.
One should also finish all prescription pills, though symptoms may disappear earlier. Moreover, ensure you keep in touch with your health care provider as advised for evaluation of the progress made.
If you have a severe case of oral thrush, a weakened immune system, or if the condition is recurring, your healthcare provider may conduct further investigations to identify potential underlying causes and develop a comprehensive treatment plan.
Risk factors
- Weakened immune system: Oral thrush is common among individuals who have low immunity, like people living with HIV/AIDS, cancer, and autoimmune disorders.
- Antibiotic use: Antibiotics may cause imbalance of microorganisms in the body such as the good bacteria that inhibit growth of Candida and therefore can lead to further yeast proliferation and ultimately mouth thrush.
- Corticosteroid use: Corticosteroid steroids should be avoided for a prolonged period since they have been associated with the suppression of immunity and creation of favorable conditions for the growth of candida.
- Diabetes: It is understood that uncontrolled diabetes causes high sugar levels in saliva which creates favorable environment for yeast development.
- Dry mouth: Oral thrush occurs more frequently among individuals who have reduced saliva production either through medical conditions or as a drug complication because saliva is one of the factors in maintaining equilibrium in the oral environment.
- Poor oral hygiene: Failure to observe good oral hygiene can result in a buildup of yeast, bacteria, and stuck food particles in the mouth which is conducive to the growth of oral thrush.
- Smoking: Smoking weakens the immune system and causes modifications in the oral milieu; a compromised host makes smokers prone to develop oral thrush.
Prevention Of Oral Thrush
- Maintaining good oral hygiene: Brushing of teeth, tongue, and gums regularly as well as flossing would go a long way in minimizing formation of plaques and in turn reducing the possibility of oral thrush.
- Proper denture care: Regular cleaning and disinfection of dentures should be practiced for persons who wear dentures in order to hinder growth of Candida on the denture surface.
- Managing underlying health conditions: The susceptibility to oral thrush can be reduced by controlling conditions such as diabetes, HIV/AIDS, among other immune-compromising illnesses.
- Avoiding certain irritants: Restriction from using irritating substances including tobacco, alcohol, and few mouthwashes may reduce oral thrush.
- Maintaining a healthy diet: Taking a balanced diet with adequate vitamins and minerals may improve the overall immune response and thus prevent oral thrush.
- Regular dental check-ups: Regular check ups with the dentist can be effective for timely detection and prevention of any dental problems like oral thrush.
Therefore, by adopting these preventive steps, people can minimize the chances of developing oral thrush and ensure that they take care of their oral hygiene.
Conclusion:
Oral thrush is also referred to as a fungal infection which may result in pain and suffering in the areas of the mouth and throat. It manifests itself in the appearance of white lesions and is associated with candidiasis, low immunity, specific medicine intake, diseases like AIDS. Prompt diagnosis is important and includes clinical examinations and swab test. There are effective treatment approaches such as antifungal drugs, proper dental care, saltwater solutions, and diet alteration that may considerably reduce the signs of this condition. Also, one should take care of oral hygiene, properly control comorbidities and avoid factors provoking oral candidiasis. Individuals can thereby maintain their dental hygiene and avoid developing candidiasis by adhering to such practices.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the primary cause of mouth thrush?
Mouth thrush arises when candida organism that lives naturally in the mouth grows excessively. Asymmetry in the microbiota may lead to overgrowth of Candida species with consequent outbreak of thrush.
-
Is oral thrush caused by stress?
The oral thrush mostly occurs because of more than enough yeast Candida, which usually result from low immunity, some medicines, and other health problems. Though stress can lower one’s defense mechanisms, it does not necessarily lead to oral thrush.
-
Is oral thrush permanent?
In most cases, oral thrush is treated by using antifungals and good oral hygiene practices. Nevertheless, such infection can become chronic in persons with reduced immunity level or pre-existing pathological disorders that require ongoing treatment strategies and precautionary approaches.







