What is an ECG Test?
September 12, 2023
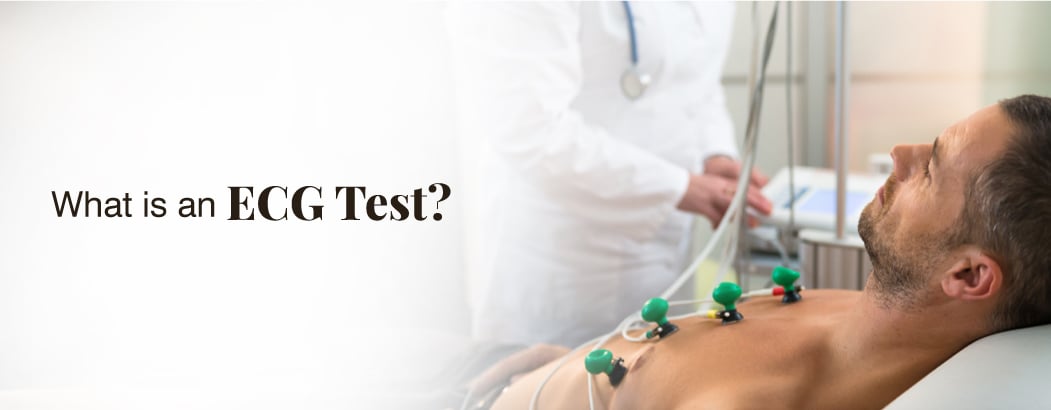
What is ECG Test?
A common medical examination called an electrocardiogram checks the electrical pattern of the heart. Holter monitoring is commonly referred to as a non-invasive procedure involving the placement of electrodes at the patient’s body surface and recording of the heart’s electric activity. This article seeks to analyze different segments that constitute an ECG test, such as its execution, analysis of outcomes, utility, technological improvements, and relevance in medicine.
Table of Contents
- What is ECG Test?
- How is ECG Test Performed?
- Interpretation of ECG Results
- Application of ECG Test
- Advancements in ECG Technology
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
During a successful ECG test, a technician will put electrodes in certain parts of a person’s chest, armpits, and legs. These electrodes are linked to a recorder of electrical signals, which is generated by the heart. This is a short test that lasts only for a couple of minutes, is painless, and does not pose any danger.
The test is performed using an electrocardiogram (ECG) by a machine that records the changes in the current of the heart. The various waves and intervals in this graph indicate the various stages of the heartbeat. It is useful in determining the rate, rhythm, and problems associated with the rate of the heart.
Interpretation of ECG Results
The testing machine generates a line diagram that represents the electrical activity of the heart. The cardiac cycle consists of numerous waves, each indicating a phase of this process. It is a source of useful data on the heart’s rhythm and rate as well as anomalies if they exist.
Since it is very difficult for an average non-specialized person to interpret an ECG on their own correctly, interpreting an ECG test normally requires the help of a medical specialist like a cardiologist or an electrophysiologist. This involves examining the different components of an electrocardiogram so that the presence of any irregularities and signs of heart disorder can be established. These may include cardiac arrhythmias, damaged heart muscle, and low flow indications to the heart.
Application of ECG
Applications of ECG tests cover cardiology as well as general healthcare. They are typically applied in identifying and tracking conditions such as arrhythmia, heart attack, heart failure, and congenital heart defects in the heart. Additionally, ECGs may serve to screen people who are at high risk for heart disease or as a routine medical evaluation.
Besides the diagnosis of heart disorders, ECG’s are also helpful when evaluating how treatments work, monitoring the progress of cardiac rehabilitation, and providing directions on medicinal administration or additional examinations. Often, before a surgical procedure to determine whether the patient’s heart is strong enough to withstand surgery, an ECG test will be taken.
Test Advancements in ECG Technology
ECG technology has significantly improved over the years, leading to a high level of precision and efficacy as a diagnostic tool. In a conventional ECG, different electrodes are positioned on the chest, arms, and legs. Nonetheless, wearable ECG devices exist that permit prolonged monitoring for weeks or months.
Therefore, ECG patches or smartwatches are convenient wearable devices that benefit both patients and healthcare professionals. They are more useful for people with suspected heart rhythm abnormalities that may not be captured during an in-office ECG test. The data from these devices can be sent to healthcare providers for analysis and interpretation.
Conclusion
ECG test remains an important resource for cardiology that gives information concerning the electrical activity of the heart. It is a non-invasive and painless procedure which is of critical importance in diagnosing and monitoring various heart problems. ECG monitoring is now increasingly affordable and convenient with technological advances, enabling constant and distant assessment of cardiac wellbeing.
If you have worries about your cardiac well-being or are experiencing pain in the chest or palpitations, visit a physician and determine whether an examination with an electrocardiogram is required. Therefore, early diagnosis and medical management of heart diseases often result in a better prognosis as well as an improved quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What does an ECG test measure?
The electrical activity of the heart is assessed using an ECG test.
2. Is an ECG test painful?
However, as we can see, an ECG test is non-invasive.
3. Who interprets ECG results?
Cardiologists and electrophysiologists usually interpret ECG results.
4. Can ECGs detect all heart conditions?
A lot of heart conditions can be detected using ECGs, but not all. A full assessment requires additional tests.
5. Can I wear an ECG device at home?
Indeed, wearable ECGs permit monitoring heart activity at home.
6. How often should I have an ECG test?
However, the frequency of ECG testing is associated with specific risk factors and the medical history of individual patients. Consult with your healthcare provider for individualised advice.
7. Can ECG results vary from person to person?
Yes, ECG results, too, differ with age, gender, and general well being. These results should, therefore, be compared to a baseline so as to get an accurate interpretation.








