What is a stroke?
August 22, 2022
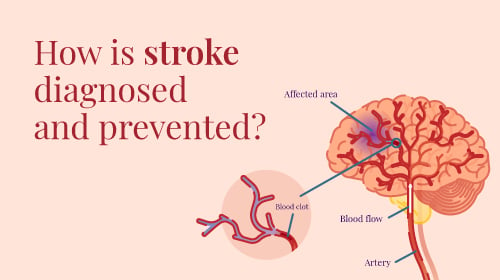
An obstruction in the blood flow to the brain or the rupture and bleeding of a blood vessel may cause a stroke. The rupture or obstruction prevents blood and oxygen from reaching the brain’s tissues.
The following are the three main stroke types:
- A blood clot is involved in a Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA), which usually reverses on its own.
- A clot or plaque in the arterial may block an artery, resulting in an Ischemic Stroke. The signs and complications of an ischemic stroke may persist permanently or linger longer than those of a TIA.
- A blood vessel ruptures or leaks into the brain, causing a Hemorrhagic Stroke.
Symptoms of Stroke
Reduced blood flow to the brain causes damage to its tissues. For instance, when the brain is damaged, the bodily functions it regulates exhibit stroke-like symptoms.
The better the prognosis for someone experiencing a stroke, the earlier they receive treatment. It will be easier to act quickly if you know the stroke symptoms. Among the symptoms of a stroke are:
- Paralysis
- Difficulty speaking or comprehending others,
- Slurred speech & numbness
- weakness, especially on one side of the body, in the arm, face, or leg
- Lack of clarity, disorientation, or responsiveness
- Abrupt behavioural alterations remarkably increased agitation
- Visual issues, such as double vision or difficulty seeing with one or both eyes that are blurry or blacked out
- Difficulty walking, loss of coordination, or both
- Dizziness
- Convulsions with a terrible, abrupt headache and no apparent reason
Risk factors of stroke
Diet
A poor diet can make you more susceptible to stroke. This kind of diet has much of the following:
- Cholesterol
- Saturated fats
- Trans fats
- Salt
Inactivity
Lack of exercise or inactivity itself might increase the risk of stroke.
There are several health advantages to regular exercise. First, adults should engage in at least 2.5 hours of aerobic activity per week, according to the CDC. This might be as simple as taking a few weekly brisk walks.
Excessive drinking
A higher risk of stroke is associated with heavy drinking. Therefore, if you do drink, do so moderately. This means no more than one drink per day for ladies and two for males.
Blood pressure might increase with frequent heavy drinking. Furthermore, it can raise triglyceride levels, which might cause atherosclerosis. This is artery plaque buildup, which causes blood vessels to become smaller.
Tobacco usage
Tobacco use raises the risk of stroke because it can damage the heart and blood vessels.
Personal History
Some stroke risk factors such as:
- Family background: Some families have an increased risk of stroke due to inherited health issues, including high blood pressure.
- Sex: Strokes can affect both sexes, although, in all age categories, women are more likely to experience them than men.
- Age: The probability of having a stroke increases with age.
Diagnosis
A person should seek medical attention at a hospital within three hours of the onset of their symptoms for the most outstanding results.
A doctor can utilise different diagnostic procedures to ascertain the type of stroke. These consist of:
- Medical history and physical examination: A doctor will enquire about the patient’s symptoms. They will assess your coordination, reflexes, sensation, and physical strength. Additionally, they might check blood pressure and the blood vessels behind the eyes and listen to the carotid arteries in the neck.
- Blood testing: A doctor may run blood tests to assess the likelihood of bleeding or blood clots, measure the concentrations of particular substances in the blood, such as clotting factors, and check for the presence of an infection.
- CT scan: X-rays can reveal brain tumours, haemorrhages, strokes, and other problems.
- A doctor can identify damaged brain tissue using an MRI scan, which uses radio waves and magnets to create an image of the brain.
- Carotid ultrasound: A doctor may use an ultrasound to examine the carotid arteries’ blood flow and check for plaque or narrowing.
- Cerebral angiogram: To make the blood vessels in the brain visible on an X-ray or MRI, a physician may inject a dye into the brain. The blood vessels in the brain and neck may be seen in great detail thanks to this.
- A thorough image of the heart is produced by an echocardiogram , which medical professionals can use to look for any potential origins of blood clots that may have reached the brain.
Prevention
Taking care of the underlying problems is the greatest method to prevent a stroke. People can accomplish this by changing their lifestyles in ways like:
- Consuming a wholesome diet
- Keeping a healthy weight, doing regular exercise, not using tobacco, abstaining from alcohol, or only sometimes drinking
A nutritious diet should have much of the following:
- Vegetables, fruits, and whole grains
- Nuts
Make sure to keep cholesterol and saturated fats in check, as well as the consumption of red and processed meat. Additionally, consume salt in moderation to support normal blood pressure levels.
People also ask
1. What are the three main signs of a stroke?
Sudden numbness or weakness in the arm, leg, or face, typically on one side of the body. Unexpected difficulty in comprehending, speaking, or confusion. sudden issues with one or both eyes’ eyesight.
2. What happens to you when you have a stroke?
One side of the body may experience numbness or paralysis in the face, arm, or leg. Difficulties are walking, losing balance, and vision issues in one or both eyes. A headache is not typically a symptom of a stroke, but an abrupt and severe headache can occasionally accompany some forms of stroke.
3. How long is a hospital stay after a stroke?
After a stroke, a patient typically stays in the hospital for five to seven days. The stroke care team will assess the stroke’s consequences throughout this period to decide on the rehabilitation strategy.
4. How long after a stroke are you discharged?
Stroke patients are frequently sent from the hospital to a rehab centre or home in four to seven days. It depends on how severe the stroke was and how well the patient is recovering.








