Stages of Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease in Adults.
February 21, 2024
Hand, foot and mouth Disease
Fever, decreased appetite, sore throat, and lethargy are typically the first signs of hand, foot, and mouth illness. It is possible for uncomfortable oral sores to appear following a fever. These sores, known as herpangina, typically show up as dots in the rear of the mouth. These areas may blister and cause pain.
Table of Contents
- Hand, foot, and mouth disease in adults
- Causes of Hand, foot, and mouth disease in adults
- Stages of Hand, foot, and mouth disease in adults
- Spreading of Hand, foot, and mouth disease in adults
- Complications of Hand, foot, and mouth disease in adults
- Prevention of Hand, foot, and mouth disease in adults
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
Hand, foot, and mouth disease in adults
Mouth ulcers and a painful rash on the hands and feet are two of the symptoms of hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD), a viral infection brought on by enteroviruses.Although there is no known cure for HFMD, it often goes away on its own in seven to fourteen days without medical intervention.
Adults can also contract this condition, although typically the symptoms are moderate and can be managed with rest and medication in a matter of days. Even in the absence of symptoms, adults can still spread the illness.
Causes of Hand, foot, and mouth disease in adults
Hand, foot, and mouth illness is brought on by enterovirus 71 and coxsackievirus A16. The gastrointestinal system plays a major role in the disease’s transmission.
Hand, foot, and mouth disease is a common illness in young children, particularly those under the age of five. The inability of the body’s immune system to combat the virus means that adults can still contract the illness.Adults with hand, foot, and mouth disease are more prone than children to experience major complications from the condition, which can be fatal if treatment is delayed.
Women who are pregnant are the adults most susceptible to hand, foot, and mouth illness. When a pregnant woman has hand, foot, and mouth disease, the foetus may experience major difficulties like: an elevated risk of infection, stillbirth, or miscarriage
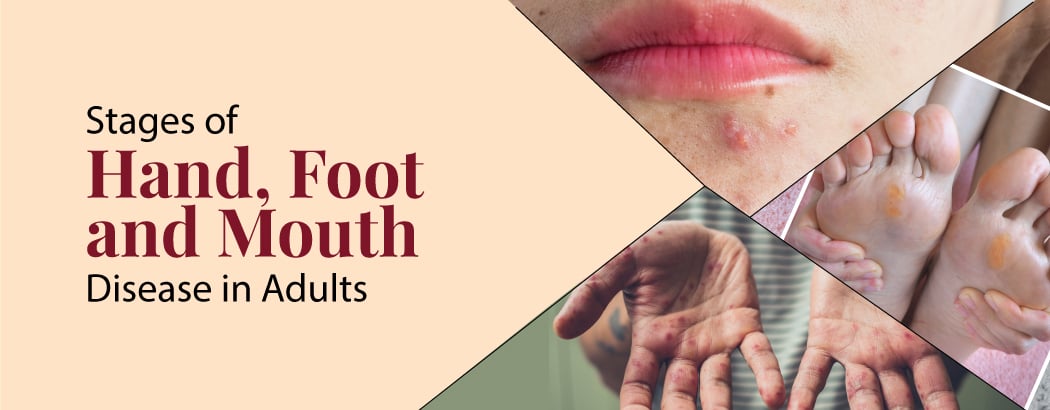
Stages of Hand, foot, and mouth disease in adults
Hand, foot, and mouth illness typically lasts three to seven days and is moderate. Not everyone experiences symptoms. Some individuals carry the virus but show no symptoms.Following are the different stages of HFMD in adults:
- Fever: You will initially get a fever that lasts three to five days. A scratchy throat, a sense of fever, an appetite loss, and a decrease in water intake are some of the symptoms.
- Mouth Sores: Mouth sores will appear a few days after the fever first appears. Usually, they begin as little red dots on the tongue and insides of the mouth. They blister and hurt more and more with time.These sores can cause decreased appetite, increased drooling, and a preference for drinking mainly liquids since they make it difficult to chew and swallow meals. It’s best to get your kids checked out right away if you see any of these symptoms so that the illness can be treated before it becomes worse.
- Skin Rash: A hand, foot, and mouth disease infection may cause rashes on many body areas. These rashes are noticeable on the palms, the bottoms of the feet, and in certain situations, the buttocks, legs, and arms.Because the sickness can spread to other parts of the body through the blisters that emerge from the rashes, it’s critical to keep them clean and untouchable.
Spreading of Hand, foot, and mouth disease in adults
The following are the ways in which HFMD spreads:
- coughing
- sneezing
- blisters
- mucus (sputum or phlegm)
- saliva
- poo (faeces)
Complications of Hand, foot, and mouth disease in adults
Complications from HFMD are rare most of the time.The biggest risk is dehydration. The following uncommon consequences are also seen in some cases:
- Encephalitis or paralysis like polio
- Loss of fingernails or toenails
- Aseptic meningitis caused by a virus
If a pregnant person has had HFMD symptoms or has come into touch with an infected person, they should notify a medical practitioner.
Prevention of Hand, foot, and mouth disease in adults
Numerous preventative techniques for HFMD are also effective in warding off other ailments, such as the common cold. Some of these techniques are:
- Avoiding close contact with those who have HFMD is one way to lower the chance of contracting an infection.
- Another is washing your hands thoroughly and often.
- Frequently cleaning and disinfecting high-touch surfaces
Conclusion
A frequent viral infection is hand, foot, and mouth disease. Though it occasionally affects adults and older children, infants and young children are the most vulnerable.
By avoiding sick individuals, often washing their hands, and abstaining from sharing food or beverages, people can lower their chance of getting the virus.Managing the symptoms, if any, is the usual course of treatment. In roughly seven to ten days, a person should recover.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can adults with HFMD go to work?
Despite the fact that the majority of individuals with HFMD may not exhibit symptoms, they may nevertheless be communicative and able to infect others.
Even when their symptoms subside, people can still spread infection for several days or weeks.To prevent the disease from spreading, those who have HFMD should stay home alone and refrain from going to work.
How can a doctor diagnose HFMD?
A physical examination is typically used by a doctor to make the diagnosis of HFMD.They may check the hands, feet, and genitalia for blisters or sores. Along with the sores, they might also look for other typical symptoms.
Occasionally, a laboratory test could be required to verify a diagnosis. Physicians may take faeces and throat samples for analysis, or they may search for relevant antibodies or viral components in the blood.
Is HFMD contagious?
Yes, HFMD is contagious.Personal contact is how it spreads, although maintaining excellent hygiene will help reduce your risk of contracting it







