Sickle Cell Disorders
June 21, 2020
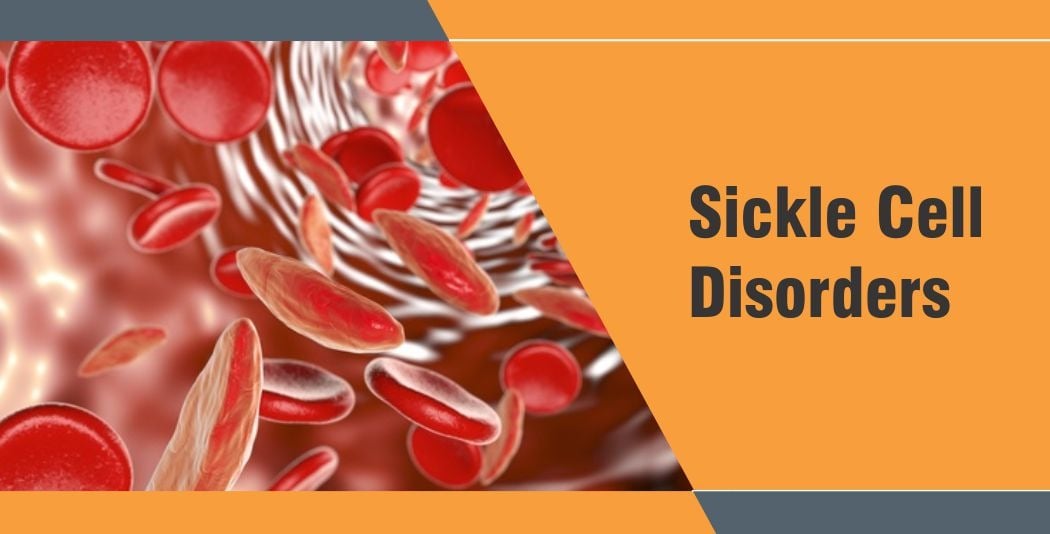
A sickle cell disorder is one legacy no parent will want to bequeath to children and no child will want to inherit from parents, but sadly, it is one of world’s leading genetic diseases passed on from one generation to the next. Most people are not aware of the disorder or its symptoms
Sickle cell disease
Sickle cell disease is an inherited disease in which your red blood cells (RBC) are misshapen. RBCs have haemoglobin, which carries oxygen to the tissues in the body. In normal cells, haemoglobin is round, smooth and flexible so it glides along the blood vessel easily. If you have sickle cell disease, haemoglobin is shaped like rods and they stick together. This gives RBCs a rigid abnormal ‘C’ shape, making it tougher for the cells to flow through the blood vessels easily, especially the narrow vessels. As the RBCs are shaped like sickles, the disorder is called sickle cell disorder or sickle cell disease.
Inherited not caught
Sickle Cell Disease is an inherited genetic disease. That means you are born with it. You cannot get it after birth. A problem in chromosome 11 causes abnormal haemoglobin molecules. You can have sickle cell disease only if you get a defective gene from both your parents. If you get a defective gene only from one parent, then you will have sickle cell trait. You will not have the disorder, but will be a carrier. You can pass it on to your children if your spouse also has the trait.
Effects of sickle cell disease
- The abnormally shaped RBCs block blood vessels hindering blood flow to organs.
- The cells die quickly, within 10-20 days, while normal RBCs live for 90-120 days. The rate at which they die is faster than the rate at which new cells are formed
Symptoms of Sickle Cell Disease
Symptoms appear early, within the first few months after birth. They include
- Irritability
- Swollen hands and feet
- Yellow skin and whites of eyes
As the child grows, the symptoms increase and they include:
- Breathing problem
- Dizziness
- Fast heart rate
- Fatigue
- Irritability
- Pale skin
- Delayed growth
- Delayed puberty
- Frequent infections
- Vision problems
- Bouts of pain called Pain Crisis
Pain Crisis
If you have sickle cell disorder, pain will be your unwelcome and regular visitor. When the sickle cells block a blood vessel cutting of blood supply to tissues and organs, they become oxygen starved. This results in intense sudden pain that can be sharp or throbbing. These episodes are called pain crises and can occur in the arms, stomach, chest, lower back or legs depending on the position of the block. The pain can last a few hours or weeks and may sometimes require hospitalization.
Complications of Sickle Cell Disorder
Sickle Cell Disorder increases your chances of stroke, heart disease, blindness and bone problems as blood flow to organs can be compromised often leading to kidney, liver, heart, lung and spleen damage.
What does it mean if you have sickle cell trait?
You will not have the disease, but you may want to be prepared when you start a family.
A simple blood test will let you know if your partner has sickle cell trait.
If both have the trait, then your baby has a 25% chance of being born with the disease and 50% chance of inheriting the trait
If one of you has the trait, then your baby will not have the disease, but will have a 50% chance of having the trait and becoming a carrier.
Talk to your doctor for guidance and support.
If you do not have sickle cell disorder or trait
Be aware of the symptoms of sickle cell disease so that you can help someone you know recognize it and give their baby the right treatment at the right time.
Can Sickle cell disease be cured?
There are some medications which are useful in tiding over a pain crisis, some which decreases the severity of disease, but these do not cure the disease.
The only permanent cure for Sickle cell disease is Bone Marrow Transplantation, especially for people with severe symptoms. Recent advances in donor selection and treatment protocols have vastly improved the outcome of Sickle cell disease rendering it completely curable.







