Hydrosalpinx
April 7, 2020
What is Hydrsalpinx and why is it a concern?
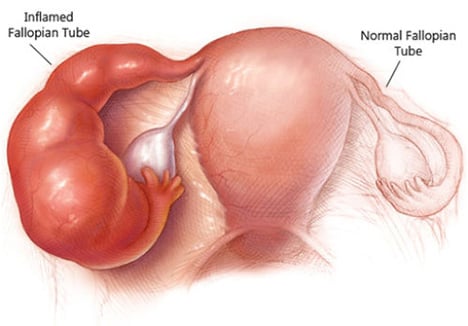
When the fallopian tubes get blocked or damaged, swollen and filled with fluid, it is called Hydrosalpinx. Fallopian tubes are attached to the uterus on either side and are responsible to pick up the eggs from the ovary every month and this is where the sperm meets the egg.
The fertilization happens in these tubes and the embryo travels across the fallopian tubes and enters the uterus where it gets attached to the wall and develops into baby. This process is not possible when the tubes are blocked and this poses a major concern for couple who find it difficult to have a baby. This results in abnormal pregnancies with complication Eg. Ectopic pregnancy which mostly can be life threatening.
How common is this?
Tubal disease is responsible one third of all female factor infertility, and the prevalence of hydrosalpinx is as high as 30% in women with tubal pathology. Although in‐vitro fertilization (IVF) was first developed to treat tubal infertility, it was soon observed that patients with hydrosalpinx had a poor outcome after IVF treatment
What Causes Hydrosalpinx?
Usually any damage to the tubes, infection or inflammation will result in swollen and fluid filled tubes. Other reasons like surgeries directly in the tubes, adhesions of the uterus wall or pelvis, sexually transmitted infection or other infections like TB or Chlamydia.
What are the symptoms of Hydrosalpinx?
Usually females with Hydrosalpinx go asymptomatic for a longer period till they start the process of fertility treatment or conception. Difficulty in fertilization or infertility is the first sign of Hydrosalpinx. Few Many females may sometimes present with pelvic pain and unusual vaginal discharge.
These symptoms occur after a period
- Pain during ovulation and menstruation
- Bloating
- Changes in colour or smell of the vagina
- Low back pain
- Fever
- Nausea
- Painful Intercourse
The impact of Hydrosalpinx with Fertility and IVF
Since Fallopian tubes play a vital role in the process of fertilization blocked tubes causes increased rate of failures with IVF procedures. Hydrosalpinx needs to be treated, disconnected by blocking or clipping and removed before starting the IVF procedures, which can increase the success rates drastically.
If the Hydrosalpinx goes untreated, this condition will compromise the IVF efforts, sometime the fluid may leak into the uterus during embryo transfer or after into the uterine cavity and leads to many complications and poor outcome.
How is Hydrosalpinx ruled out?
- Ultrasound where the sac is viewed and identified a sausage shaped larger areas.
- Hysterosalpingogram – This is a form of X-Ray test, where the uterus and fallopian tubes are filled with dye and are viewed and examined under X-Ray.
- Laparoscopy to view the fallopian tubes directly, mostly done as a confirmation test.
How is it treated?
If the Hydrosalpinx is small, the affected part can be repaired to allow normal pregnancy. In some cases, removal of the affected part is made mandatory under laparoscopy.
If you are experiencing a dull aching pelvic pain and are finding difficult to conceive, do not delay and visit the fertility specialist immediately.
If you are experiencing any unusual pain in your abdomen or pelvic area call +91 9384681770 and fix a consultation right away. Remember, an early diagnosis can help detect the presence of any conditions like Hydrosalpinx and help cure it at its early stages. This ensures to keep your fertility intact. Rela fertility expert will be able to talk through the different treatment options and help you choose the one best for your situation.