Carotid Endarterectomy (CEA)
March 23, 2020
Overview of Carotid endarterectomy
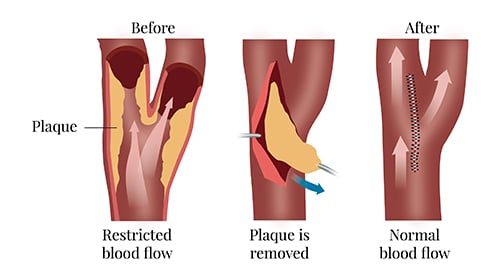
Carotid endarterectomy is a procedure to treat carotid artery disease. This disease occurs when fatty, waxy deposits build up in one of the carotid arteries. The carotid arteries are blood vessels located on each side of the neck.
This buildup of plaque may restrict blood flow to your brain. Removing plaque causing the narrowing in the artery can improve blood flow in your carotid artery and reduce your risk of stroke.
In carotid endarterectomy, you receive a local or general anaesthetic. The surgeon makes an incision along the front of the neck, opens your carotid artery and removes the plaques that are clogging your artery. Then, your surgeon repairs the artery with stitches or a patch made with a vein or artificial material (patch graft).
Sometimes surgeons may use another technique called eversion carotid endarterectomy. This involves cutting the carotid artery and turning it inside out, then removing the plaque. Your surgeon then reattaches the artery.
The most common cause of carotid artery stenosis is Atherosclerosis which causes plaque to form within the wall of the carotid artery. Generally, it is an age-related degenerative change and other non-modifiable risk factors like Type II Diabetes, Hypertension can aggravate the disease process. Smoking, alcohol consumption, obesity are the modifiable risk factors that aggravate the progression of atherosclerotic changes and thus cause Carotid Artery Stenosis.
With the reduction of the calibre of the major blood vessels that supply to the brain the demand for oxygen supply to the brain decreases. When the stenosis is less it can cause temporary symptoms like transient ischemic attacks (TIA) of the brain, spinal cord and retina and is often the early indicator before a Major brain stroke.
Contents
- What is Carotid Endarterectomy
- Why Carotid Endarterectomy
- Carotid Endarterectomy Procedure Steps
- Carotid Endarterectomy Diagnosis
- Is carotid endarterectomy major or minor surgery?
- What is the recovery time for carotid endarterectomy?
- What is a common postoperative complication of carotid artery disease?
- What do you monitor post carotid endarterectomy?
- What is the success rate of carotid artery surgery?
What is Carotid Endarterectomy
Carotid endarterectomy (CEA) is a Neurosurgical procedure done to correct the stenosis(narrowing) of the Internal Carotid Artery(Chief blood supply) to the brain to reduce the risk of ischemic stroke of the brain.
It is surgery done in the neck at the bifurcation of the common carotid artery where the main blood supply to the brain (Internal carotid artery) originates. The artery is opened at the area of stenosis and the atherosclerotic plaque is completely removed followed by the closure of the artery with fie sutures. The results were very good if this procedure was done under high magnification in Modern Neuromicroscopes
Why Carotid Endarterectomy
The North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial (NASCET) found that patients who have symptoms of stroke and high-grade Carotid stenosis (>70% block) significant benefit from this surgery and there is almost 17% decrease in major brain strokes and a 7% decrease in deaths due to major strokes. European Carotid Surgery trial (ECT), Asymptomatic Carotid Atherosclerosis Study (ACAS) and many other major trials were done and have established the usefulness of this surgery.
National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) guidelines recommend patients with moderate to severe (50–99% blockage) stenosis, and symptoms should undergo treatment at the earliest.
Also Read: Migraine – Symptoms, Causes And Treatment
Carotid endarterectomy procedure steps
Step 1
Carotid endarterectomy is an operation during which the surgeon removes the fatty deposits to correct the narrowing and to allow blood and oxygen to flow freely to the brain.
Step 2
These two main arteries, one on each side of the neck, deliver blood and oxygen to the brain.
Step 3
Plaque builds up in large- and medium-sized arteries as people get older, more in some people than others depending on lifestyle and hereditary factors.
Step 4
This build up is a vascular disease called atherosclerosis, or hardening of the arteries.
Step 5
The procedure takes about 2 hours to perform but may seem slightly longer depending upon the anasthetic and preparation time. For carotid endarterectomy, a general anaesthetic or a local anaesthetic (to numb the neck area) may be used.
Carotid Endarectomy Diagnosis
- If people remain awake during the Carotid endarterectomy operation, the surgeon can better evaluate how the brain is functioning.
- The surgeon makes an incision in the neck over the area of the artery that contains the blockage and an incision in the artery. The blockage is removed, and the incisions are closed. For a few days afterwards, the neck may hurt, and swallowing may be difficult. Most people can stay in the hospital for 1 or 2 days.
FAQ
-
- Is carotid endarterectomy major or minor surgery?
Most studies on outcomes of carotid endarterectomy (CEA) have focused on the major complications of death and stroke. Less is known about minor but more common surgical complications such as hematoma, cranial nerve palsy, and wound infection.
-
- What is the recovery time for carotid endarterectomy?
Most people will be able to return to work 3 to 4 weeks after having a carotid endarterectomy. The surgeon or general physician will be able to advise you further about returning to work. Being active can help your recovery, but you shouldn’t overdo it.
-
- What is a common postoperative complication of carotid artery disease?
Postoperative complications of CEA, including myocardial infarction; perioperative stroke; postoperative bleeding; and the potential consequences of cervical hematoma, nerve injury, infection, and carotid restenosis.
-
- What do you monitor post carotid endarterectomy?
Postoperative care should include monitoring of the patient’s neurologic status, blood pressure control, and wound observation for hematoma.
-
- What is the success rate of carotid artery surgery?
A carotid procedure may reduce the long-term risk of stroke from 2% per year to 1% per year. A procedure is most likely to benefit people who have 60% to 70% or more narrowing of the carotid arteries.








