Difference Between Bypass and Open Heart Surgery
May 2, 2025
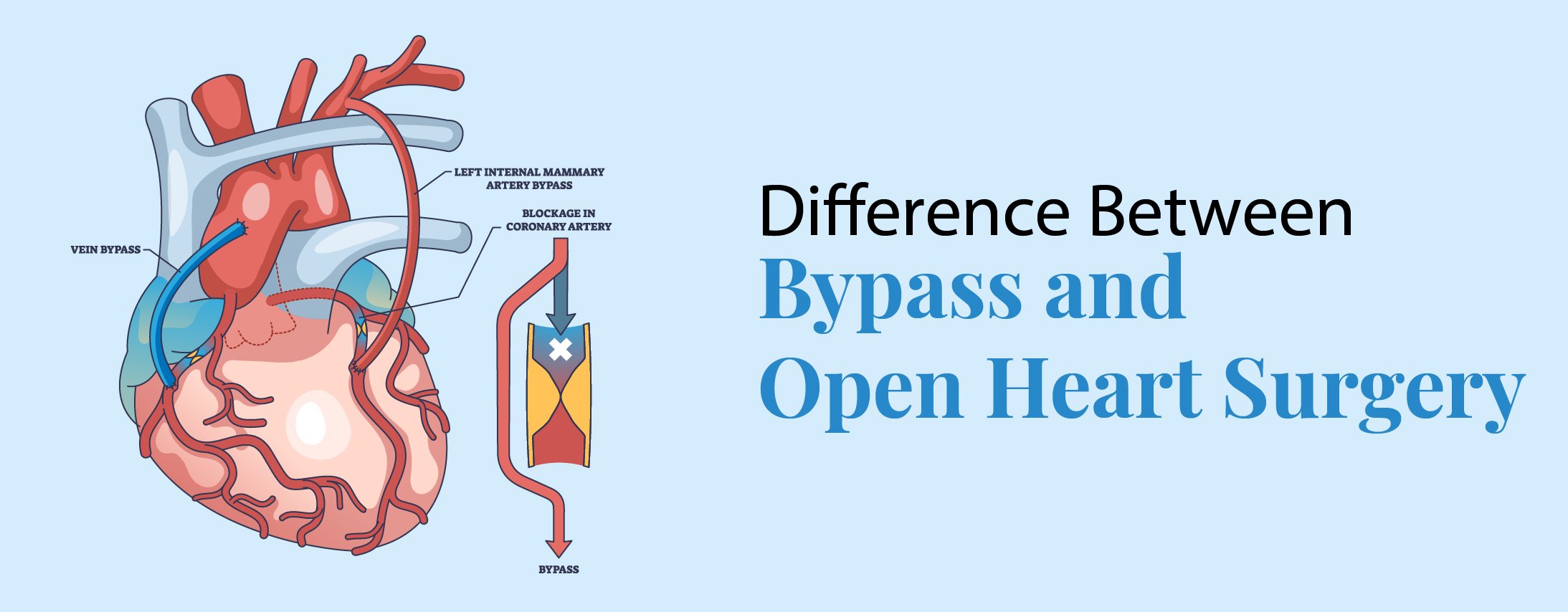
Difference Between Bypass and Open Heart Surgery
Surgery may be required to restore normal heart function in severe cases of heart disease, a common health concern. People are often informed about two major surgical procedures: open-heart and bypass. Although the heart is engaged in both, their roles and techniques are distinct. This blog post will look at the key differences between these two methods.
What is Bypass Surgery?
The purpose of bypass surgery, also known as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), is to improve the heart’s blood flow. It is performed when plaque formation causes the coronary arteries to narrow or become clogged, limiting the amount of oxygen reaching the heart muscle.
During bypass surgery, a healthy blood vessel is grafted, usually from the arm, leg, or chest, to create a new route around the obstructed artery. This improves overall heart function and reduces the likelihood of heart attacks by enabling blood to circulate freely.
What is Open-Heart Surgery?
Any surgical approach that requires opening the chest to operate on the heart is referred to as “open-heart surgery.” It refers to a variety of heart procedures, including bypass surgery, rather than a single surgery.
A heart-lung machine may be utilized to replace the heart’s pumping action while the treatment is being administered. During open-heart surgery, the surgeon makes an incision in the chest. Open-heart surgery can be used for many conditions, such as:
- Heart valve repair or replacement
- Congenital heart defect correction
- Heart transplant
Key Differences Between Bypass and Open-Heart Surgery
- Purpose: Bypass surgery is specifically performed to restore blood flow by bypassing blocked arteries, while open-heart surgery is a general term for multiple heart procedures.
- Procedure Type: Bypass surgery is a specific type of open-heart surgery, whereas open-heart surgery encompasses various operations that require opening the chest.
- Use of Heart-Lung Machine: In bypass surgery, the use of a heart-lung machine depends on the technique used. Open-heart surgery, especially complex procedures, often requires it.
- Conditions Treated: Bypass surgery is mainly used to treat coronary artery disease (CAD), while open-heart surgery is performed for various heart conditions, including valve disease, congenital defects, and heart transplants.
- Recovery Time: The recovery time for bypass surgery is generally 6 to 12 weeks, whereas open-heart surgery recovery varies based on the procedure performed.
How to Know Which Surgery is Needed?
The patient’s heart condition dictates whether bypass surgery or another sort of open-heart surgery is appropriate. Typically, bypass surgery is recommended if the condition is congested coronary arteries. Other types of open heart surgery may be required if the heart has structural issues, such as congenital abnormalities or valve failure.
To determine the appropriate course of action, doctors will use imaging exams, stress tests, and other diagnostic tools.
Conclusion
Although they are related, open-heart surgery and bypass surgery are not identical. While open-heart surgery is a broad word that refers to a range of heart therapies, bypass surgery is a specific type of open-heart surgery used to unclog blocked arteries. Knowing these distinctions will help you and your loved ones make informed decisions and discuss your options with your doctor if you or they require heart surgery.
Preventing the need for these surgeries in the first place is possible by maintaining good heart health through regular exercise, a balanced diet, and health screenings. However, modern medical advancements provide safer surgeries and better recovery results if surgery is required.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is a heart-lung machine always used in these surgeries?
Not necessarily. In bypass surgery, a heart-lung machine may or may not be used, depending on the technique. In complex open-heart surgeries, the machine is often required.
2. What lifestyle changes are needed after heart surgery?
Patients are advised to adopt a heart-healthy diet, exercise regularly, quit smoking, and manage stress to prevent further heart issues.
3. Are there risks involved in these surgeries?
Like any major surgery, both bypass and open-heart surgery carry some risks, such as infection, bleeding, or complications related to anesthesia. However, advancements in medical care have improved safety and recovery outcomes.